
Similarly, when an animal gets cold and wants to warm up or on seeing a predator, they desire to warn the predator to step off, the little muscle at the base of every single hair follicle will constrict and eventually pull the hair erect.

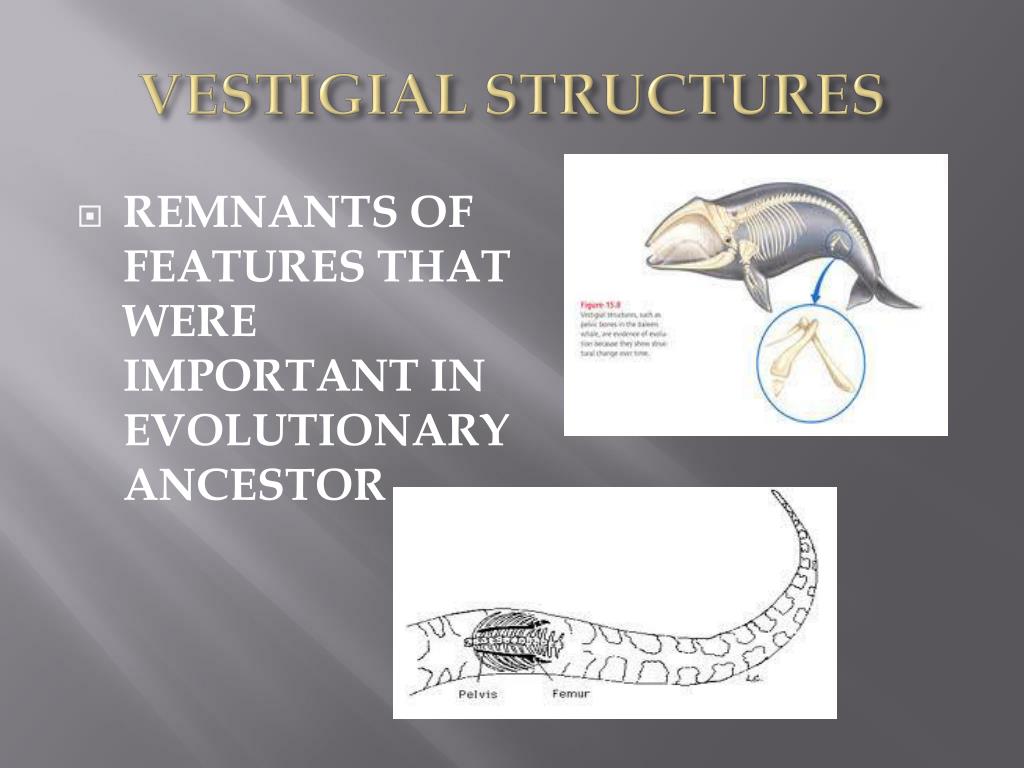
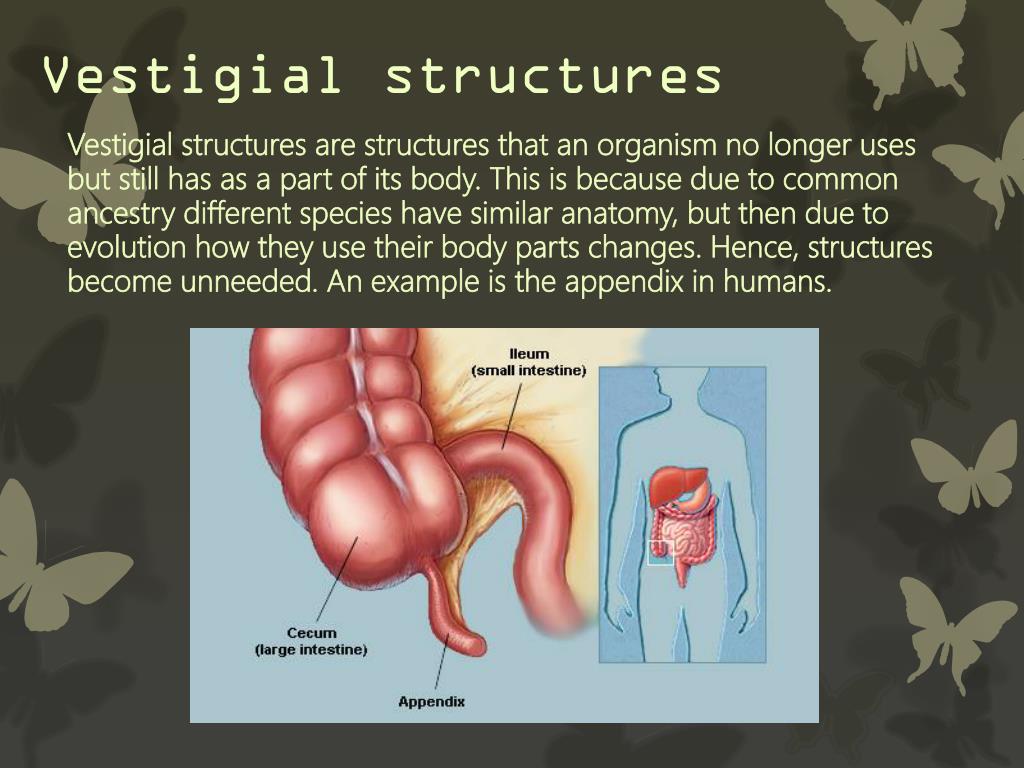
The other vestigial organs specifically in human are canine teeth, body hair, nipples in male, coccyx, panniculus carnosis, vermiform appendix, auricular muscles, wisdom teeth and many more. The vital significance of such organs is that the major hints regarding the evolution of organisms or the evolutionary history of the organisms can be known.įor example goosebumps which is more of a reflex rather than an organ but is still regarded as vestigial in humans about which we will discuss below in detail. The idea of these organs would be well suited to argue for a beginning creation when the organisms were well designed structurally but after a hundreds or thousands of years, the genetic information shrinking or corrupting gradually lead to less functionality. The need for the presence of vestigial organs in our body has terminated in the current era but due to the inherited trait of the ancestors, we are bound to carry the remains of it. Even if there are hundreds of vestigial organs in modern organisms, the evolution would not be proved so easily because evolution requires the organs to grow better with an addition of functional design. In other words, these organs are primarily the non-functional organs in modern species however they were considered well developed and functional during the period of the existence of ancestor species of our evolution.
The various sub-types of it are:Īs the name suggests, vestigial refers to the organs that rendered functions during the evolutionary history but in modern era, the roles of such organs are not as fundamental. In this article, the main consideration will be the first classification of the evolution, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
